

However, that can be a good approach, because the default controls look different among various browsers. If you don't specify this attribute, no controls will appear - and you will instead have to create your own controls and program their functionality using the Media API (see below).
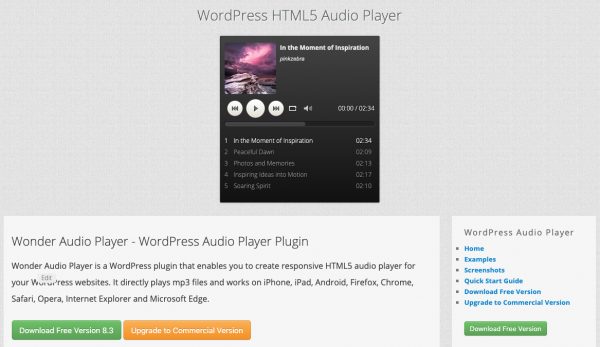
If the element is not supported then and will be ignored.If omitted, most browsers will attempt to guess this from the file extension. type is used to inform the browser of the file type.src contains the path to the audio file to be loaded (relative or absolute).We do this using the element, which takes the attributes src and type.The two formats that will give maximum coverage are mp3 and ogg vorbis. To ensure reasonable coverage, we should specify at least two different formats. Here we define an element with multiple sources - we do this as not all browsers support the same audio formats.
#Chrome html5 player not working mp4#
(Currently, browsers that support mp3 also support mp4 audio). MP4 files typically contain AAC encoded audio.

Right-click then choose properties, and then define a meta-data called 'type/vtt'. Go to your subtitles file inside your directory on AWS. Note: You can also use an MP4 file instead of MP3. Turns out you will have to change your configuration in the AWS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
